Privacy Policy
FAQ
Join Mailing List
Certifications
Application
Cross Reference
Sample Request
Contact Us
中文
- About Us
-
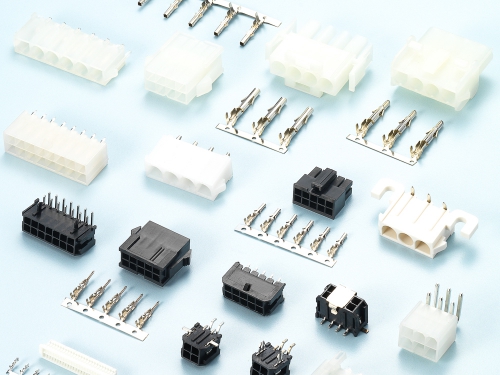
High Power
200Amp/180Amp/30Amp Straight Type 9192 Series 180Amp Screw mount Type 9192 Series 16Amp Switch Type 9192 Series Busbar Conductor 9192 Series
High Power BTB Connectors 65AMP to 150AMP
150Amp High Current Type D 9113-D+9114-D Series 100Amp High Current Power 9310 Series 90Amp Blade Type Power 9397 Series 75A(AC)/45A(DC) Ultra High Power+ 9303-C Series 75Amp High Flow Power HFP® 9113-E+9114-E Series 65Amp High Power + Connector 9303 Series 65Amp BackPlane Power 9396 Series
High Power BTB Connectors 15AMP to 60AMP
60Amp Max P60™ 9395 Series 60Amp High Flow Power HFP® 9113-F+9114-F Series 45Amp High Flow Power HFP® 9113+9114 Series 30Amp High Power Connector 9391-A Series 20Amp HVDCP® 9113-C+9114-C Series 20Amp Rapid Power connector 9113+9114 Series 15Amp Power Pin 4191 Series
55Amp 3KW/3600W Power+Signal Card Edge 9305 Series 48A+24A 2KW Power+Signal Card Edge Connector 9307 Series 33Amp 3200W Power+Signal Card Edge Connector 9309-A Series 30Amp Card Edge Hybrid CEH™ 9392 Series 25+100Amp 18+60Amp AC+DC Power 9394 Series 12.5Amp HFCE® High Flow Card Edge-Power+Signal 9302 Series 12.5Amp HFCE® High Flow Card Edge-Power 9393 Series 12Amp 2KW Power+Signal Card Edge Connector 9309 Series
-
High Speed
HSMV™ 28+Gbps 2337 Series HSER™ 28+Gbps 2386 Series HSMV™ 25Gbps 2384-A Series 1.27mm 25Gbps 2322 Series Hermaphroditic 25Gbps 2330 Series Rapid 25Gbps 9211 Series HSMV™ 25Gbps 2336 Series HSMV™ 25Gbps 2384 Series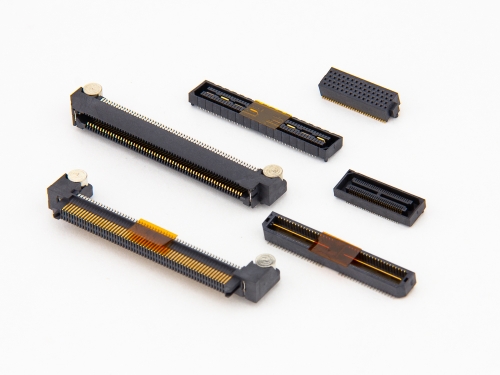
Card Edge 8206 8208 8216 8236 8406 Series NGFF(M.2) 8402-C Series Mini PCI Express 8402-A Series PCI Express 8406-C Serie PCI Connector 8206 Series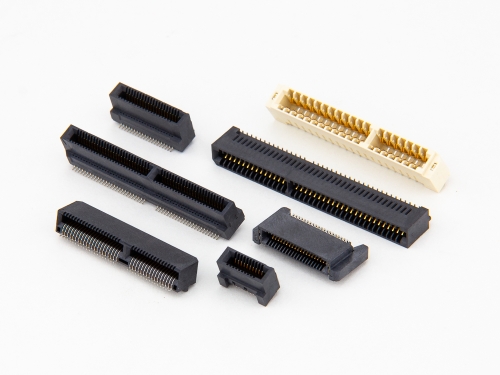
-
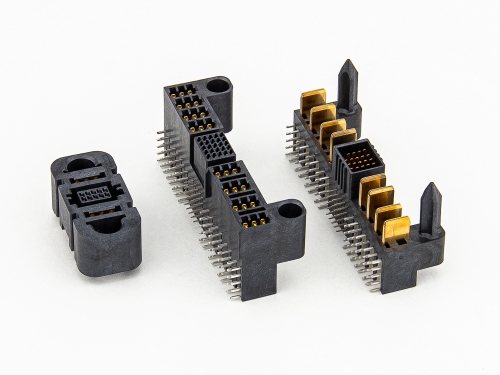
BackPlane
Hard Metric Type A 9111-7 Series Hard Metric Type AB 9111-7 Series Hard Metric Type B 9111-7 Series Hard Metric Type C 9111-7 Series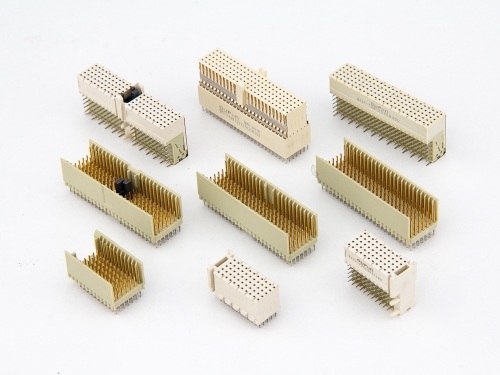
Hard Metric Type D 9111-10 Series Hard Metric Type DE 9111-10 Series Hard Metric Type E 9111-10 Series Hard Metric Type F 9111-10 Series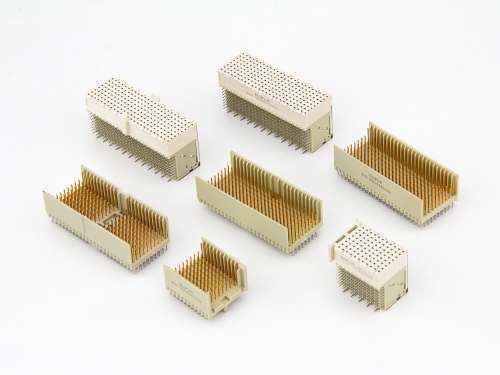

Hard Metric Type L to N, Others
Hard Metric Type L 9111-7 Series Hard Metric Type M 9111-7 Series Hard Metric Type N 9111-7 Series Coding & Special Contact 9111 Series Power Modules 9111-3 Series Hard Metric Shroud 9111-7 Series -
Automotive, I/O
Automotive Shrouded Connectors 5290 Series Fakra Connectors 5100 Series Automotive Headers 5090 Series Automotive PCB Socket 2042 Series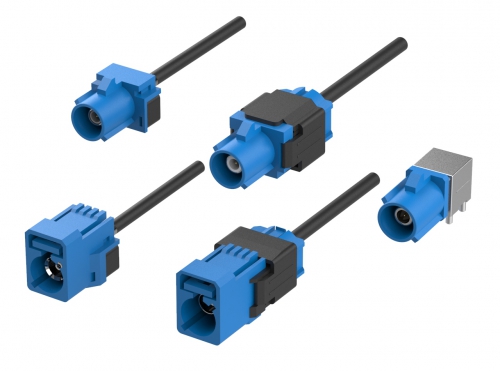
USB 4.0: Type C Waterproof 8976WP-C Series USB 4.0: Type C 8976-C Series USB 3.2 : Type C Waterproof 8975WP-C Series USB 3.2 : Type C 8975-C Series USB 3.2 : Micro AB and B types 8973 Series USB 3.2 : A and B types 8972 Series USB 2.0 : Type C Waterproof 8975WP-C Series USB 2.0 : Micro AB and B types 8971 Series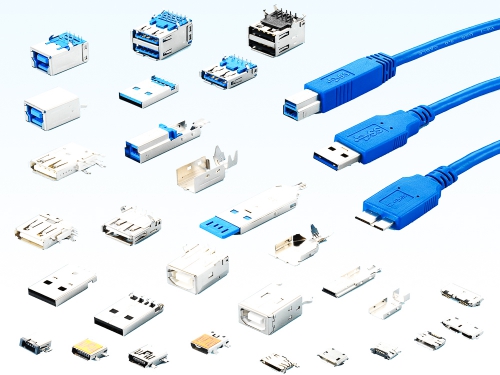
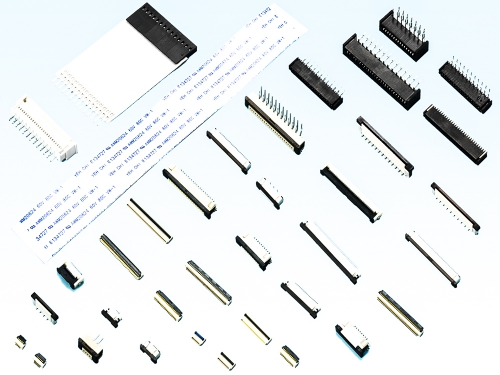
IDC Type 7901 Series Straight Type 7905 7915 7925 Series R/angleType 7906 7916 7926 7936 Series Solder Cup Type 7907 7917 Series CrimpType 7908 7918 Series Slim Type 7902 7912 Series D_Sub Cover & Dust Cover DP Series
-
Board to Board
0.35mm Connector 2394 Series 0.4mm Connector 2379 Series 0.5mm Floating Board To Board 2631 Series 0.50 mm mezzanine connector 2332 Series
0.8mm Floating Board To Board 2681 Series 0.80mm mezzanine connector 2381 2382 2383 Series 1.0mm mezzanine connector 2348 2349 Series 1.27mm SMC Single Row Connector 2321-A1 Series 1.27mm SMC Dual Row Connector 2321-A Series
0.80x1.20mm Header 2081 Series 1.0mm (0.039") Header 2411 Series 1.27mm (0.05") Header 2211 2212 2214 2215 Series 2.0mm (0.079") header 2111 2112 2113 2114 2115 2116 2118 Series 2.54mm(0.100") Header 2011 2012 2015 2016 Series 5.08mm (0.200") Header DLC Series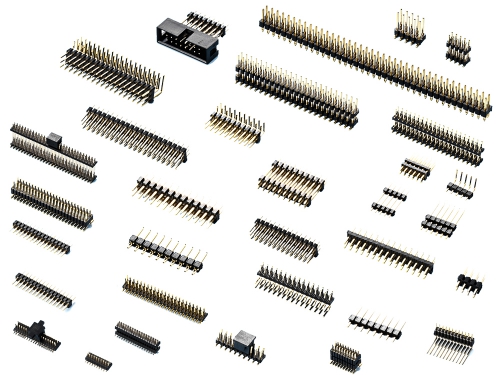
Box Header 1.27mm 2216 3216 Series Box Header 2.00mm 3112 Series Box Header 2.54mm 2013 3011 3012 Series
-
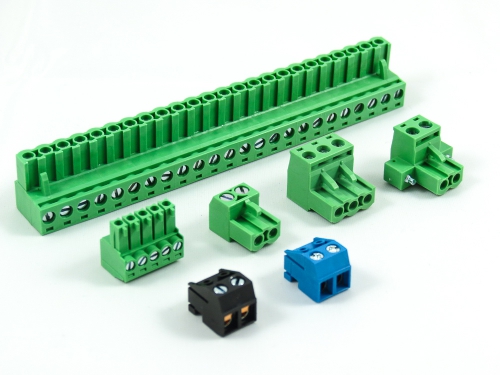
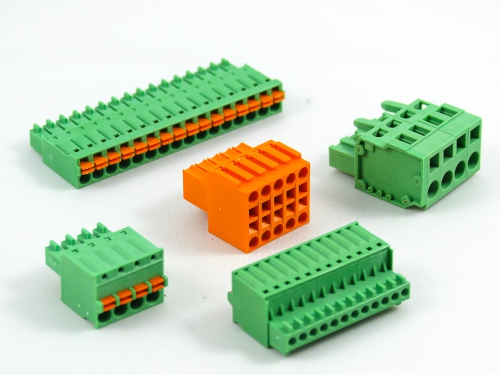
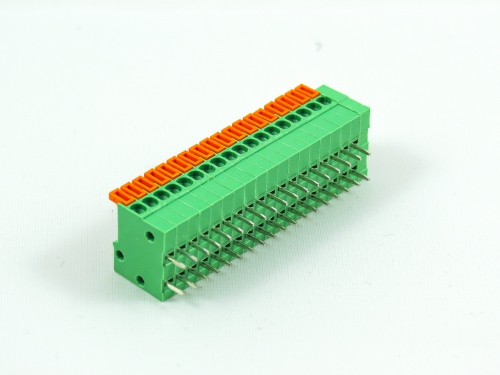
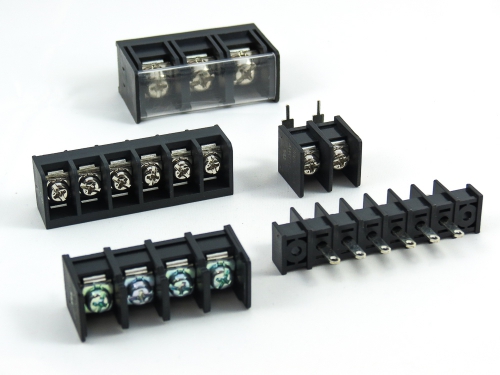
Terminal Blocks
3.50mm 8930-C Series 3.81mm 8930-D Series 5.00mm 8930-F Series 5.08mm 8930-G Series 7.50mm 8930-I Series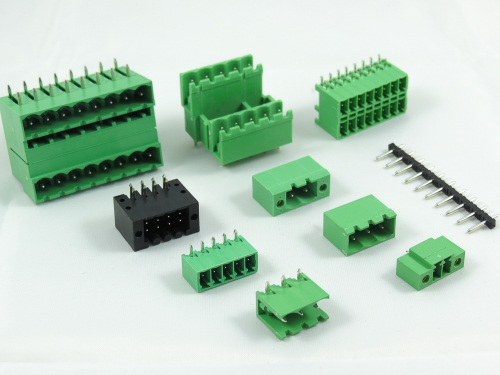
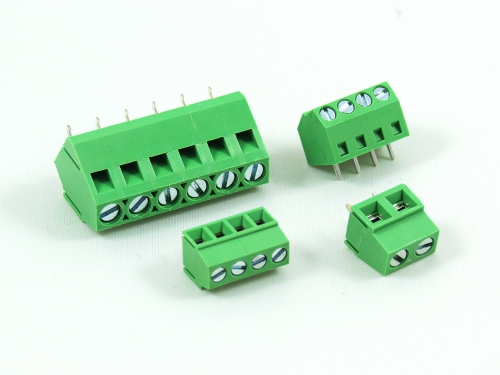
Fixed Type Rising Clamp PCB Mount
3.50mm 8932-C Series 5.00mm 8932-F Series 5.08mm 8932-G Series 6.35mm 8932-H Series 7.50mm 8932-I Series 7.62mm 8932-J Series 9.52mm 8932-V Series -
Cables,Wires,Others
Connectors, IDC Cable Assembly
IDC Socket 1001 1101 1203 1204 Series IDC Plug 3016-A 3017-A Series Micro Match 6022 Series Transition Plug 6111 6211 Series Flat Cable FC FC1 FC4 Series Cable Assembly
Wire To Board Connectors 0.80mm to 2.54mm
0.8mm 4876 Series 1.0mm 4472 4473 Series 1.25mm 4573 4574 4575 Series 1.5mm 4572 Series 1.8mm 4190 Series 2.0mm 4172 Series 2.54mm 4071 4072 4073 4074 4077 Series